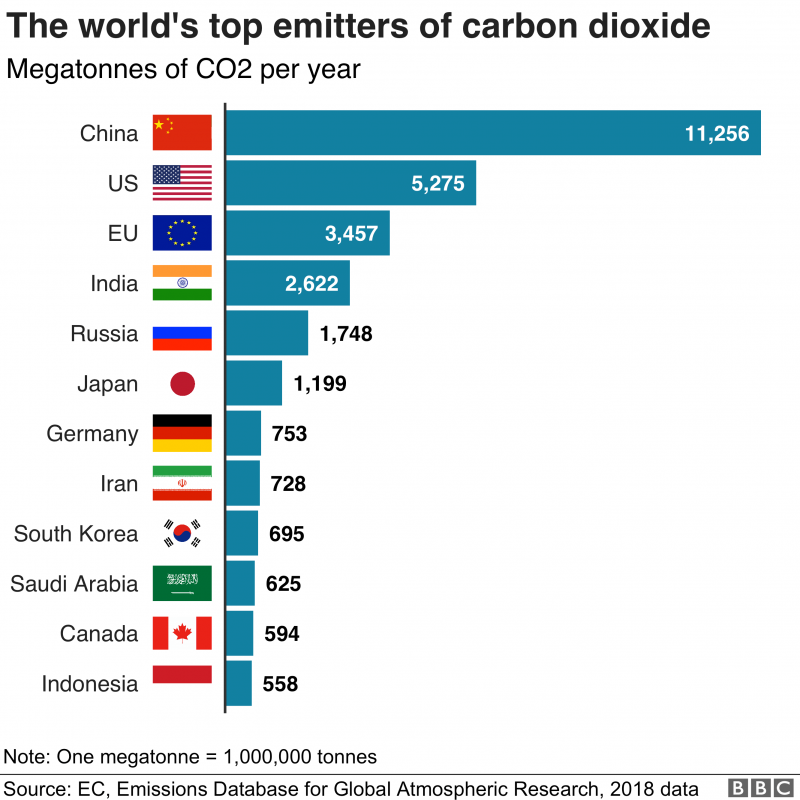
Governments have a responsibility to provide their citizens with basic needs and to protect them from threats.
Climate change is a new threat that is forcing many governments to take notice.
We know that climate change does not affect people equally.
Governments must consider poor and marginalized people who live in areas that are most vulnerable to climate change. This is known as climate justice.
What are some ways governments take action?
Governments can…

- Promote innovation in green technologies such as renewable energy.
- Set standards that companies will have to follow.
- Develop policies for land use, conservation, disaster management, and others.
- Build public awareness, share information and best practices
- Develop market policies such as carbon tax, and cap and trade (explained below).
Let’s look at some of these government policies!
Incentives For Green Practices
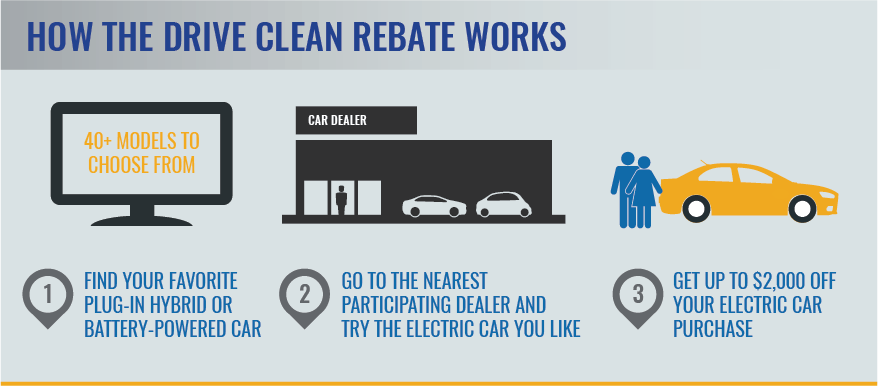
Have you ever heard the term incentive? An incentive is a reward for performing a certain action.
Sometimes these incentives are in the form of tax credits, grants, or low-interest loans.
These practices include using renewable energy sources, investing in energy-efficient buildings, developing products from recycled materials, or reducing pollution.
Governments can encourage individuals with incentives for purchasing an electric car or installing solar panels in their homes. They can even give consumers special privileges such as access to carpool lanes!
Governments can provide incentives to farmers for sustainable practices such as no-till farming, converting animal waste to compost and fertilizer, planting cover crops that nourish the soil, and other practices.
A Price On Carbon

A carbon tax forces users of carbon fuels to pay for the climate damage they cause by releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
With a carbon tax, gas and coal companies have to pay a fee. This extra cost may be passed down to consumers like you and me. For example, when gas companies have to pay more fees, our gas prices go up. It affects us all!
Ultimately, carbon taxes become powerful tools that motivate companies and individuals to switch to clean energy. If the tax is high, people want to switch to cleaner options.
Another approach is cap and trade. Cap is the maximum limit on greenhouse gas emissions for all polluters. Trade refers to the issuing and exchanging of permits.
In other words, the government gives permits to individual companies for how much they can emit. Companies that don’t use all their permits can sell to others who need more. This trading of permits in a carbon market encourages good behavior and helps keep emissions in check.
Global Negotiations
We know climate change is a global problem and does not respect boundaries. Hence countries have to work together.
The United Nations has brought countries together with a mission to address climate change.

It focuses on four key areas on ways to: mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, adapt to climate change, report emissions, and finance climate action in developing countries.
The Kyoto Protocol of 1997 and the Paris Agreement of 2015 have been two steps in the right direction. The goal of the Paris Agreement is to limit global temperature rise to well below 2°C by the end of the century.
However, these efforts have met with challenges. Lack of cooperation among member countries, lack of enforcement, and politics have made it difficult to make significant progress.
Also, many developing countries do not like being asked to reduce their emissions. They hold developed nations like the U.S and Europe responsible for the current climate crisis.
In the next section, let us look at how companies can step up to the challenge of addressing climate change.
Summary
- Governments need to protect their people from climate change, especially those who are most at risk.
- Governments can encourage “green” behavior in companies and people by giving them financial rewards.
- Governments can tax companies who emit too much carbon, and work with other countries to find global solutions.

Governments have a responsibility to provide their citizens with basic needs and to protect them from threats.
Climate change is a new threat that is forcing many governments to take notice.
We also know that climate change does not affect people equally. Governments have to consider the poor and marginalized people who live in areas that are most vulnerable to climate change. This is known as climate justice.

What are some ways that governments take action?
Governments can...
- Promote innovations in green technologies such as renewable energy.
- Set regulations such as emission standards that companies will have to follow
- Develop policies for land use, conservation, disaster management, and others.
- Build public awareness, share information and best practices
- Develop market policies such as carbon tax, and cap and trade to encourage green behavior (explained later).
Let’s look at some of these government policies.
Incentives For Green Practices

Have you heard the word incentive? An incentive is a reward for performing a certain action. These incentives could be in the form of tax credits, grants, or low-interest loans.
Governments can provide incentives to companies that promote green practices. These practices include using renewable energy sources, investing in energy-efficient buildings, developing products from recycled materials, or reducing pollution.
Governments can encourage individuals with incentives for purchasing an electric car or installing solar panels in their homes. They can even give consumers special privileges such as access to carpool lanes!
Governments can provide incentives to farmers for sustainable practices such as no-till farming, converting animal waste to compost and fertilizer, planting cover crops that nourish the soil, and other practices.
A Price On Carbon

A carbon tax forces carbon emitters to pay for the climate damage caused by releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
With a carbon tax, gas and coal companies have to pay a substantial fee. This extra cost may be passed down to consumers like you and me. For example, when gas companies have to pay more fees, our gas prices go up. It affects us all!
If the price is set appropriately, carbon taxes become powerful tools that can motivate companies and individuals to switch to clean energy sources.
Another approach is "Cap and Trade." Cap is the maximum limit on greenhouse gas emissions established by the government. Trade refers to the issuing and exchanging of permits.
The government gives permits to individual companies for how much they can emit. Companies that don’t use all their permits can sell to others who need more. If a company exceeds its allowance of greenhouse gases, it will have to pay a steep fine.
This trading of permits in a carbon market encourages companies to reduce emissions and invest in new technology and punishes those who heavily pollute the atmosphere.
Global Negotiations
Climate change is a global issue. Governments have a responsibility to work with other countries and global organizations to find solutions.

The United Nations has brought countries together with a mission to find ways to: reduce greenhouse gas emissions, adapt to climate change, report emissions, and finance climate action in developing countries.

The Kyoto Protocol of 1997 and the Paris Agreement of 2015 have been two steps in the right direction. The goal of the Paris Agreement is to limit global temperature rise to well below 2°C by the end of the century.
However, such international efforts have met with challenges. Lack of cooperation among member countries, lack of enforcement, and politics have made it impossible to make significant progress.
In addition, many developing countries do not like being asked to reduce their emissions. They hold developed nations like the U.S and Europe responsible for emitting greenhouse gases since the Industrial Revolution that has led to the current climate crisis.
In the next section, let us look at how companies can step up to the challenge of addressing climate change.